Artificial Intelligence Information Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly become one of the most important fields in technology today. From enhancing business operations to transforming industries like healthcare, finance, and entertainment, AI is driving significant change across various sectors. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, understanding the fundamentals of AI, its applications, and its potential impact is crucial in this era of digital transformation.
In this article, we will explore the basics of AI, discuss advanced concepts, and delve into how AI is reshaping the world we live in. Let’s embark on this journey to better understand the power and potential of artificial intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence Information
What is Artificial Intelligence?

Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and perform tasks that typically require human intellect. The goal of AI is to create systems that can solve problems, learn from experience, and improve over time—essentially mimicking human thinking.
At its core, AI is about enabling machines to perform tasks that traditionally required human intelligence, such as recognizing speech, translating languages, making decisions, and understanding visual inputs.
There are two primary types of AI:
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, refers to AI systems designed to perform a specific task or a narrow range of tasks. These systems are highly specialized and do not possess general reasoning or understanding. Examples include facial recognition systems, chatbots, and voice assistants like Siri or Alexa.
General AI (Strong AI)
General AI, or Strong AI, is a more advanced and theoretical concept. It aims to create machines that can perform any intellectual task that a human can. Unlike narrow AI, general AI would have the ability to understand and reason across a wide range of problems, much like humans do. While we’re not there yet, researchers are actively working towards this goal.
How Does Artificial Intelligence Work?
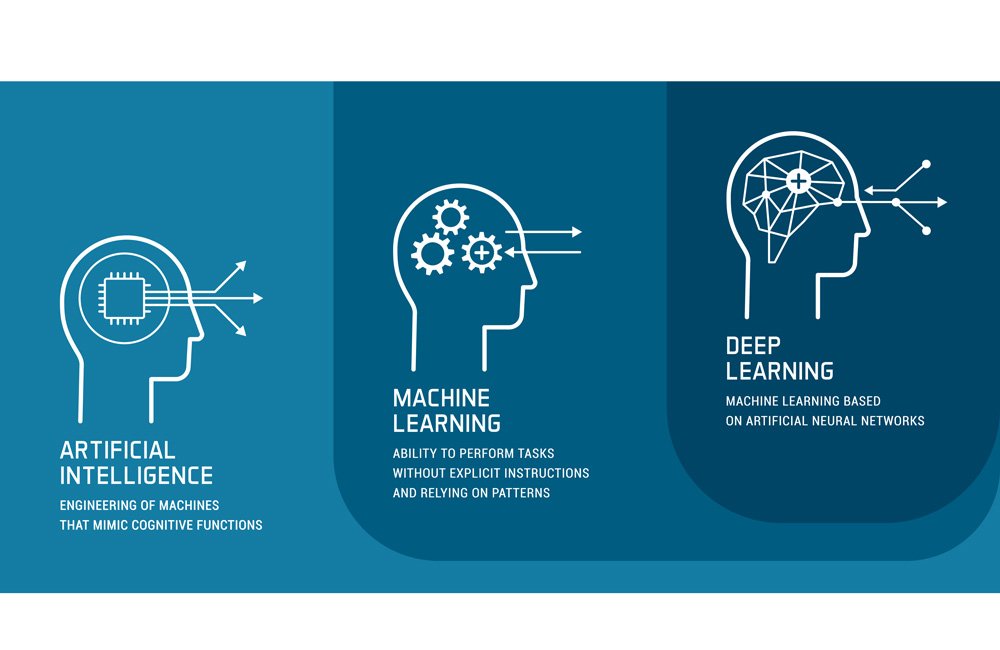
Artificial Intelligence works by mimicking cognitive functions through algorithms, data, and machine learning models. The fundamental components of AI include:
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that allows machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. It involves training algorithms on data to help them identify patterns and make predictions or decisions.
There are several types of machine learning:
- Supervised Learning: In this approach, the algorithm is trained on labeled data, which means the input data has corresponding known outputs. The system learns to predict outputs from the given input.
- Unsupervised Learning: In unsupervised learning, the algorithm works with data that does not have labels or predefined outputs. The goal is to uncover hidden patterns or structures in the data, such as grouping similar items together.
- Reinforcement Learning: This approach is based on the concept of trial and error. The system learns by interacting with its environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. Over time, it seeks to maximize the total reward.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. NLP plays a critical role in AI-powered chatbots, virtual assistants, and language translation systems. It combines linguistics with machine learning to make sense of text and speech, allowing AI to process human language in ways that were once thought impossible.
Computer Vision
Computer Vision is a field of AI that enables machines to interpret and understand visual information. This includes tasks such as object detection, facial recognition, and scene analysis. Using digital images or videos, AI systems can recognize patterns, detect faces, and even read text within images.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence

Artificial Intelligence is transforming a wide range of industries, offering solutions to complex problems and improving efficiency. Some of the most notable applications of AI include:
Healthcare
AI is revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, improving patient care, and automating administrative tasks. Machine learning models can analyze medical images to detect early signs of diseases such as cancer, while natural language processing helps doctors quickly find relevant medical literature. AI is also used in personalized medicine, where treatment plans are tailored based on individual genetic profiles.
Finance
In the financial sector, AI is being used for fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and risk assessment. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of transaction data to identify patterns that might indicate fraudulent activity. AI-powered chatbots also improve customer service by assisting clients with routine inquiries and transactions.
Transportation
AI plays a crucial role in autonomous vehicles, where machine learning and computer vision systems enable cars to navigate and make decisions in real-time. AI is also used in traffic management systems to optimize routes, reduce congestion, and improve safety.
Retail
AI is helping retailers offer personalized shopping experiences by analyzing customer behavior and preferences. Recommendation algorithms suggest products based on past purchases, while chatbots assist customers with queries. AI is also used in inventory management and supply chain optimization, ensuring that products are available when and where they are needed.
Challenges in Artificial Intelligence
Despite its remarkable capabilities, AI also faces several challenges that hinder its full potential:
Data Privacy and Security
AI systems often require vast amounts of data to train and improve their performance. This raises concerns about data privacy and security, particularly when sensitive information is involved. Protecting user data from breaches and misuse is an ongoing challenge.
Bias in AI
AI algorithms can inherit biases present in the data they are trained on. If the data is biased or unrepresentative, AI systems can produce unfair or discriminatory results. Addressing bias in AI is critical to ensuring that these systems are ethical and equitable.
Job Displacement
As AI continues to automate tasks that were once performed by humans, there are concerns about job displacement. While AI has the potential to create new jobs, it also threatens to replace roles in industries such as manufacturing, customer service, and transportation.
Lack of Transparency
Many AI systems, particularly deep learning models, are considered “black boxes” because it can be difficult to understand how they arrive at decisions. This lack of transparency makes it challenging to trust AI systems, particularly in critical applications like healthcare and law enforcement.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
As AI continues to evolve, its impact on society is expected to grow exponentially. The development of general AI, while still far off, would mark a major milestone in human history. In the meantime, advancements in narrow AI (Artificial Intelligence)will continue to improve productivity and efficiency across industries.
In the near future, AI is likely to play a larger role in solving global challenges, such as climate change, healthcare access, and education. However, its rapid development also necessitates careful consideration of the ethical, legal, and societal implications that come with it.
Also Read : The Future Of Higher Education: Trends In University Learning
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is transforming the world in profound ways, from automating routine tasks to solving complex problems. Understanding the basics of AI, its techniques, and its applications can help you better appreciate its potential and limitations. As AI continues to develop, it will become an even more integral part of our lives, revolutionizing industries and reshaping society. However, with this progress comes the responsibility to ensure that AI is used ethically and transparently to benefit everyone.
FAQs
What is the difference between narrow AI and general AI?
Narrow AI is designed to perform specific tasks, such as facial recognition or language translation. General AI, on the other hand, would have the ability to perform any intellectual task that a human can, with a broader understanding and reasoning capacity.
How does machine learning relate to artificial intelligence?
Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on developing algorithms that allow machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time. It’s one of the key technologies that powers many AI systems.
Is AI safe to use?
AI can be safe if used responsibly. However, there are concerns around data privacy, bias, and transparency in AI systems. It’s essential to develop AI technologies that are ethical and designed with safeguards to ensure they are used responsibly.
Can AI think like humans?
Current AI systems cannot think like humans. While AI can process data and make decisions, it does not possess consciousness, emotions, or general reasoning abilities. AI is designed to simulate aspects of human intelligence but is not capable of human-like thought.
What industries are most impacted by AI?
AI is transforming many industries, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and retail. It is being used to automate tasks, improve efficiency, and create personalized experiences.







